Residency news and updates:
- October 27th will be a reverse conference with scavenger hunt. Princess shift will be from 7am-12pm, conference will be afterwards around the boardwalk.
- 7a: Resident Lecture – Brenda – Harlem Trauma Diaries / Faseeh – CCU EKG lecture #1
- 8a: Dr Rizzo – Radiology Rounds
- 9a: Dr Cocchiara – ED Trauma Management
- 10a: Dr Nguyen – The Eye (part 1)
- 11a: Med student lectures: Tanzeela – Seizures / Tanzina – Sickle Cell pain crisis
Resident Lecture – Brenda – Harlem Trauma Diaries
- Always ABCDE
- Case 1: 40M Stab in neck and laceration to right UE with tourniquet
- Screaming “I can’t breath”
- Classically: Zone 2 = OR
- CTA everybody if stable, if platysma violated
- Hard signs = Go to OR
- Became hypotensive/tachycardia → started MTP
- Case 2: 23M “jumped over bunch of garbage cans”
- Edema on right thigh
- Took Kratom (can → QTc prolongation, serotonin syndrome)
- http://www.emdocs.net/toxcard-kratom-2/
- Kratom = kind of like PCP + Loperamide
- Case 3: 80M huge hematoma side of face
- IOP = 60
- Complete visual loss within 60-100 mins
- Indications for lateral canthotomy:
- IOP >40
- Proptosis
- Contraindications:
- Globe rupture
Faseeh – CCU EKG lecture #1
- STEMI vs OMI
- Dr. Smith’s ECG Blog: The OMI Manifesto
- STEMI criteria (70% sensitivity for occlusion, doesn’t include STEMI equivalents which can benefit from reperfusion)
- ER physicians more sensitive at calling STEMI
- ECG changes in ACO
- Wellens syndrome: DO NOT stress test (they have critical LAD stenosis which → MI), go straight to cath lab
- Spodick’s sign: downsloping TP segment, esp in II, seen in ~30% pericarditis
- “Witting found that Spodick’s sign occurred in 29% of patients with pericarditis and 5% of patients with STEMI” (LIFTL post)
- Benign Early Repolarization:
- Fish-hook pattern esp in V4, very typical, BER findings more prominent when bradycardic
,
- T wave will be more prominent than STE
- Concave ST segment
- Asymmetrical T wave
- No Terminal QRS Distortion
- Absence of both an S wave and J wave in either of leads V2 or V3
- Left Ventricular Hypertrophy: voltage criteria and one non-voltage
- Sokolow-Lyon: S wave in V1 and tallest R wave in V5 and V6 >35 mm
- Common Criterias used: Left ventricular hypertrophy
- Sensitivity of criteria (numerous studies): Accuracy of ECG criteria for the diagnosis of left ventricular hypertrophy: a comparison with magnetic resonance imaging
- Non-voltage: 2 criterias
- Increased R wave peak time > 50 ms in leads V5 or V6
- ST segment depression and T wave inversion in the left-sided leads: AKA the left ventricular ‘strain’ pattern
- Sokolow-Lyon: S wave in V1 and tallest R wave in V5 and V6 >35 mm
- STE > 20% of QRS complex then OMI in LVH – STEMI criteria not sufficient in severe LVH
Dr Rizzo – Radiology Rounds – Upper Extremity XRs
- Scapula fracture = rare = 1% of fractures
- Associated with high velocity trauma
- Palpate scapula on elderly FOOSH injuries
- Scapula fracture.. Now look for neurovascular injuries and other injuries
- Check if violate glenoid fossa, may need ORIF
- Scapulothoracic Dissociation
- Laterally displaced scapula with an ipsilateral clavicular fracture, AC joint separation or sternoclavicular joint disruption
- Clavicle fracture
- Neonate, clavicle fx 2/2 breech delivery
- Fetal Macrosomia
- Check for brachial plexus injury
- Mid-clavicle fracture plus pneumothorax
- Humerus fractures
- Humerus ossifications centers: complete at 13-14
- 3rd most common bone that elderly fracture
- OR indications – for proximal humerus fractures
- Comminuted fractures
- Greater tuberosity fractures (w/ displacement or angulation)
- Test Axillary nerve, check sensation/motor
- Look for radial nerve injuries and wrist drop
- U-shaped splint with sling;
- OR indications: angulation > 20% or comminuted
- Elbow fractures
- Radial head most common in adult
- Supracondylar most common in pediatrics
- Look for posterior fat pad and and sail sign
- Anterior fat pad sign + posterior fat pad
- Capitellum fracture -> rare FRX
- Posterior long arm splint
- Olecranon fracture
- Older than 70, younger than 30?
- Ulnar nerve injury concern – assess with grip strength and sensation of 4th and 5th digits
- Posterior elbow dislocation
- Most common dislocation of elbow
- Reduce by traction/countertraction
- Tip: pt prone with arm hanging, and downward traction from wrist
- You can use saline bags/weights tied to wrist
- Essex-Lopresti: characterized by a fracture of the radial head, dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint and rupture of the antebrachial interosseous membrane
- Interosseous membrane disruption causing forearm instability, pt won’t be able to pronate and very weak grip strength
- Nightstick fracture: isolated ulnar shaft fracture, defense injury, high chance of compartment fracture
- ALWAYS get more than 1 view if possible – in any xray
Dr Cocchiara – ED Trauma: Part One
- Zero Point Survey: tools – airway, US, thoracotomy tray; ASSIGN TEAM ROLES
- Airway: prep – airway cart stocked and BVM, talk to pt (phonation)
- Oxygenation and ventilation – SpO2 and EtCO2
- Head tilt
- Jaw thrust in trauma 2/2 to cervical instability
- Airway injury – maxillofacial, laryngeal, neck – obstruction vs distortion
- Palpate – identification of landmarks
- Neck zones
- Hard signs = OR
- Assess Airway
- 3:3:2 Rule
- 3 fingers interincisor distance (IID) – aka in mouth
- 3 fingers hyoid-mental distance – aka under mandible
- 2 fingers hyoid-thyroid cartilage distance
- Ketamine (1-2 mg/kg IV) first line choice with paralytic (Roc) nearby
- Cricothyrotomy review
- “Scalper, finger, bougie” technique → tube
- Scalpel Finger Bougie Cricothyrotomy for SMACC 2014
- Use non-dominant hand to stabilize
- Technique from UoMD cadaver course (avoids using finger)
- Make incision to the membrane
- Use the side of the blade to drag the tissues superior to the incision upward toward the head
- Insert bougie
- Stabilize the neck! Use a c-collar.
- Correct technique
- Not this:
- How to clear C-spine
- NEXUS (NEXUS Criteria for C-Spine Imaging MDCalc)
- Canadian C-spine (Canadian C-Spine Rule MDCalc)
- EM:CRIT Modified C-Spine Rule
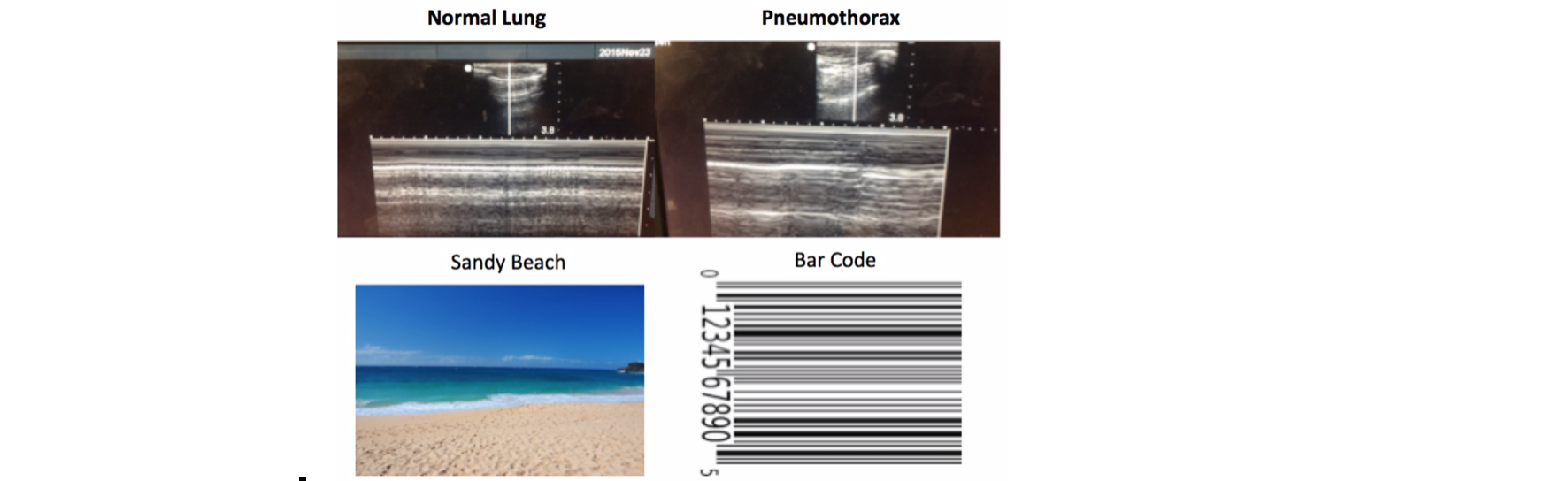
- Breathing: use US and CXR
- Sandy beach sign on US = normal
- Barcode sign = PTX
- Sandy beach sign on US = normal
- PTX/Hemothorax: needle thoracostomy -> chest tube
- Hemothorax use 28-32F (No point using larger than 28F)
- Too Big, Too Small or Just Right? Why the 28 French Chest Tube Is the Best Size (PubMed)
- Does size matter? A prospective analysis of 28-32 versus 36-40 French chest tube size in trauma
- A Prospective Study of 7-Year Experience Using Percutaneous 14-French Pigtail Catheters for Traumatic Hemothorax/Hemopneumothorax at a Level-1 Trauma Center: Size Still Does Not Matter
- Re-expansion pulmonary edema:
- Risk factors:
- Greater volume (>1L PTX volume)
- Rapid re-expansion (>1L out in first hour or two – extrapolated from hemothorax literature)
- Multiple thoracostomies
- Long-standing PTx
- Risk factors:
- Circulation
- Mentation, peripheral pulses, skin (pink/warm/dry)
- EFAST REVIEW
- If normotensive -> sensitivity 85-95%, if hypotensive → 98% sensitive
- Need 150-200cc for positive FAST
- Serial FAST exams decrease false negative
- +FAST = OR
- RUQ
- Fan through the tip – can hold 50-100 cc
- LUQ
- Suprapubic
- Subxiphoid
- Pulmonary
- Shock
- Blood products, 1 g TXA, 250 cc IVF challenge
- Goal MAP = 50 (unless TBI or spinal shock, then MAP goal = 80)
- MTP 1:1:1
- ABC score (for triggering MTP)
- Score <2 = unlikely to need MTP
- Fun links:
- Disability:
- GCS
- Exposure
- Get the patient naked, look at groin/axilla/buttocks
Dr Nguyen – The Eye (part 1)
- Vital signs of the eye
- Pupil
- EOM
- Visual acuity (download Eye Chart app or use MDcalc Snellen)
- Rosenbaum: 36”, Snellen 6’
- Visual field
- IOP
- Ocular US:
- Sheath diameter (sheath is what gets inflamed)
- >5 optic sheath = abnormal
- Vitreous hemorrhage
- Retinal detachment
- Retinal detachment vs vitreous detachment
- Sheath diameter (sheath is what gets inflamed)
- Visual Field Deficits: Identify the lesion
- Eye pain DDx: GCA, DM, Migraine, Sinusitis, Shingles, Ischemia, Neuritis
- Case 1: 70F pmhx HTN, DM, smoker presents with headache + vision changes
- Intermittently sees black from left eye for a few seconds, happened 2 weeks ago too
- Fever prior night, body aches, left eye complete blackness resolved (amaurosis fugax)
- +TTP @ left temporal artery, pulseless temporal artery
- ESR = 110, CRP elevated
- Dx: Giant Cell Arteritis
- Tx: “Rule of 50s”
- 50 years old
- ESR >50
- Prednisone 50mg daily
- If there is vision loss → Solumedrol 1000mg IV, biopsy, admission
- Amaurosis fugax = TIA of the eye
- Case 2: 31F no pmhx headache with blurry vision
- Obese and gave birth 1 year ago
- Pain with EOM
- Red desaturation test is positive
- Ocular US = optic nerve sheath swelling (>5)
- Dx: Optic neuritis
- Tx: Solumedrol 1000mg IV for 3 days, consult optho/neuro, admit
- Case 3: 28M headache + pressure behind left eye, recent URI
- +fever, congestion for 12 days, anosmia, +periorbital edema
- Vital signs of eye = normal
- Dx: Sinusitis
- No indication for CT, clinical diagnosis
- Treatment
- <10 days = tylenol/motril, nasal irrigation, flonase, decongestant
- >10 days = Augmentin or doxycycline
- Case 4: 64 yo M HA, blurry vision, photophobia
- Blurry on L side of his face, vesicular rash, fever, red in L eye (conjunctivitis)
- Eye VS = normal
- Labs: not really, just for admission
- Imaging: not necessary
- Wood’s Lamp: Dendritic lesions
- Varicella pseudodendrites – not as connected
- HSV: dendrites
- Vesicular Rash in V1 distribution of trigeminal (V)
- Dx: Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
- Tx: Rash < 1 week then acyclovir, famciclovir, or valacyclovir & Discharge
- Immunocompromised then admit
- Ramsay Hunt Syndrome = Lesions on ear or face
- Huchingsons sign = lesion on the nose
Student lecture – Tanzeela – Seizures
- Lateral tongue bite = very specific for seizure
- Status epilepticus
- >5 minutes
- Another seizure without return to baseline
Student lecture – Tanzina – Sickle Cell Crisis
- Don’t miss stroke, splenic sequestration, acute chest syndrome, priapism
- Treat pain
- Indications for stem cell transplant: