Residency updates/news:
- GI CODE reminder from Dr. Kindschuh
- Rockall >3 (10% mortality risk) → activate GI CODE
- Glasgow-Blachford >6 (50% of intervention) → activate GI CODE
- Only for UPPER GI BLEED
- Call GI code because you think you need endoscopy
- Get emergency release blood, should be within 20 minutes!
- Hgb <7 and tachycardia? Get emergency release blood!
- Hgb >7 and needs blood? Get crossmatched blood within 60 minutes
- When in doubt, check wall in resuscitation room for GI Code guidelines
- 7a: Resident Lectures – Raj – Pediatric Respiratory Distress / Mike Cat – Acetaminophen Toxicity
- 8a: EM/Cardiology STEMI series: Cath cases (on WebEx) – Dr Jeong + Cardiology Faculty
- 9a: Mike Cyd – EKG CCU lecture #3 // BREAK
- 10a: Stuart Rosenhaus – STOP THE BLEED course (w/ ability to become an instructor)
- 11a: Dr Michael – US lecture: Pregnancy Complications
- Resident Lectures – Raj – Pediatric Respiratory Distress
- Moved to 9/1/25 (Raj was overnight)
- Resident Lectures – Mike Cat – Acetaminophen Toxicity
- Suspect ingestion: found w tylenol bottle
- Airway questionably intact: GCS 8/9
- Questions we need to know:
- ABCs
- FS
- How many pills did she take?
- What time did she take them?
- Istat
- Intention
- Anything else on board (60%ish of acetaminophen overdoses have opioids involved)
- MC cause of acute liver failure in US
- Adult
- MAX dose: 4,000mg/24hr
- Single dose amounts: 325mg to 1000mg
- Children
- MAX 80mg/kg per 24hrs
- 10-15mg/kg/dose
- TJ TIDBIT: Max daily dose for someone with liver failure? 2000mg
- TJ TIDBIT: Max daily dose changes from 4000mg → 3000mg (source)
- Four stages of tylenol toxicity:
- When to treat? Need 4 hour tylenol level (Rumack-Matthew Nomogram)
- Only indicated for single, acute ingestion occurring <24 hr prior to presentation
- Consider activated charcoal if <3 hours
- Not useful for chronic ingestion
- NAC via Tox rotation:
- NAC provides cysteine for glutathione synthesis, interacts with the toxic metabolite of acetaminophen NAPQI and forms a nontoxic compound.
- What histological pattern of liver injury is caused by acetaminophen toxicity?
- Do patients recover from this liver injury?
- Increased hepatocyte necrosis–centrilobular necrosis
- When/why would you choose oral vs IV NAC?
- PO within 8-10hrs of OD; >10h post ingestion IV formulation works
- PO NAC smells like rotten eggs
- IV NAC can → anaphylactic rxn (10-20% of pts)
- The 150 Rule
- Toxic dose is 150 mg/kg
- Give NAC if level is >150 mcg/mL four hours post-ingestion
- Initial loading dose of NAC is 150 mg/kg IV (140 mg/kg PO)
- TJ TIDBIT: convulsive vs non-convulsive status, consider non-convulsive status when patient is thought to be post-ictal
- EM/Cardiology STEMI series: Cath cases (on WebEx) – Dr Jeong + Cardiology Faculty
- Interventional Conference – Presented by Wes Romney, MD CIH Cards fellow
- Multiple cases with HPI, EKG, echo, and angiogram finding
- Sgarbossa criteria sensitivity/specificity:
- Q: Is there a way in the ED to tell if you need to transfer for a complex PCI or is it after cath that you can tell?
- A: No–cannot determine high risk PCI until after cath
- A: Cath lab can do high risk STEMIs–if it is a STEMI we can cath, even if it is after a CABG.
- Q: Activate STEMI post-arrest w/ ROSC? Yes (if there is ST elevation)
- Dr. Jeong link:
- The Evolving Role of the Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory in the Management of Patients With Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest
- DAHA Statement on post-ROSC Caths summary:
- Pt with OHCA from VF/pVT with STEMI on ECG prevalence of CAD 70-85%
- Pt resuscitated after OHCA after VF/pVT without STEMI on ECG prevalence of CAD 25%-50%. Early cath is associated with a 10% to 15% absolute higher functionally favorable survival rate compared with more conservative approaches.
- Q. Is a 30% STEMI cancellation rate acceptable? (7/30? cases)
- A: 2 of the cases had STE changes
- A: Most cases did not have chest pain or stories consistent with chest pain/ACS
- Q: What if you have a good presentation, but you have a STEMI mimic (deWinters, TWI in AVL, Wellens, etc.)
- A: The state doesn’t penalize you for cases that are unclear on actual straight forward criteria; but for straight forward STEMI patients door to balloon time counts. These changes can also occur in SAH, ICH. Make sure you stabilize the patient first.
- Q: How are things going <60min DTB time?
- A: Things are going well, there are little things we need to work out…we want to make sure the patient is safe and stable prior to cath.
- Mike Cyd – EKG CCU lecture #3
- 53yoM history of colon polyps, DLD, anxiety, smoker 60 pack years, with CP and diaphoresis w nausea, exertional.
- EKG @ triage:
- Rate 75ish, normal axis, Sinus rhythm, STE in aVR, STD V4-V6, Lead I, Biphasic T wave in V2 (wellens?)
- Repeat EKG: no abnormalities seen on repeat
- Wellens Syndrome
- LifeInTheFastLane LINK (CLICK ME)
- Deeply inverted (Type B) or biphasic TW in V2, V3 (Type A) (may extend from V1-V6)
- Minimally elevated ST segment (<1mm)
- EKG pattern present in pain-free state
- Normal or slightly elevated serum cardiac markers
- Stuart Rosenhaus – STOP THE BLEED course (w/ ability to become an instructor)
- How to put on tourniquet
- QuikClot to pack wounds
- Tourniquets are rated for adults, however they can be used for some pediatric patients
- Do Adult Tourniquets Work in Pediatric Patients?
- “Adult Combat Application Tourniquets are effective at occluding blood flow even in children as young as 6 years.”
- Dr Michael – US lecture: Pregnancy Complications
- First trimester pregnancy emergencies
- US in 1st trimester
- Abdominal (curvilinear) probe
- BHCG discriminatory zone
- TAUS 4000-6500
- TVUS 1000-2000
- Sono signs of pregnancy
- Intradecidual sign (FIRST sign of preg)
- Uterus is in implantation mode (does not indicate IUP)
- Hcg <1000-2000
- Double decidual sign
- ~5 weeks
- Likely true IUP, does not confirm IUP (does not rule OUT ectopic)
- Normal GS should be oval or rounded in appearance
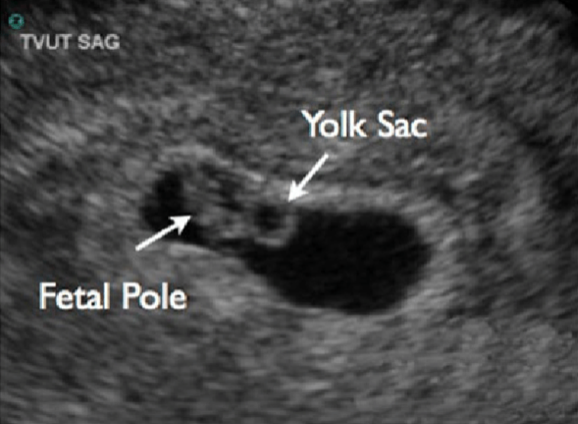
- Yolk sac (“cheerio” in the middle of double decidual space)
- FIRST definitive sign of IUP
- MUST confirm in 2x views (trans & sag)
- Fetal Pole
- 2nd structure visualized
- TV US ~ 6 weeks
- BHCG ~10,000-20,000
- Fetal Heart Rate
- TA US ~7-9 wks
- M Mode
- Normal 120-180
- Do not need to document RATE, can state “there is fetal heart activity/rate”
- Fetal viability: nonviable <24 weeks
- Endomyometrial mantle
- EMM >8mm at thinnest point
- Otherwise, suspect at interstitial ectopic
- Correlate with centrally located GS
- Measured the from the gestational sac to edge of myometrium
- ** 3 REQUIREMENTS TO CONFIRM IUP **
- 1) Gestational sac
- 2) Presence of a yolk sac OR fetal pole within the sac
- 3) EMM >8mm
- *Our role in ED is to confirm an IUP, NOT to rule out ectopic*
- Intradecidual sign (FIRST sign of preg)
- Miscarriage
- = spontaneous abortion = early pregnancy loss
- Loss of IUP within first trimester
- Overall risk: 7-27%
- Risk increases with age (35yo ~20%; 40yo ~40%)
- ALWAYS reassure patients that miscarriages are not their fault.
- No cardiac activity on US or HR <80bpm
- Management threatened abortion
- Most have normal pregnancy (3-4% have miscarriage)
- ALWAYS Check Rh status (Rh- needs RhoGAM)
- Close follow-up (within 1-2 days)
- Management missed/incomplete/inevitable
- ALWAYS Check Rh status (Rh- needs RhoGAM)
- Consult OB
- Medical vs surgical management options
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Fun facts
- 2% of all pregnancies
- #1 cause of maternal deaths in 1st trimester
- 98% in fallopian tube
- Heterotopic pregnancy: coexistence of an IUP and an ectopic pregnancy
- Usually 1/4000 to 1/30,000
- If IVF pregnancy? 1/100
- ACEP Position Statement: “Unstable patients in 1st trimester of pregnancy should be assumed to have ectopic pregnancy until proven otherwise”
- Unstable = altered mental status, hypotensive, tachycardic, ABD pain, or peritoneal signs; or presenting s/p syncopal episode
- Sen/spec for needing OR after positive RUQ FAST
- Specificity of RUQ US = 99.9%
- Sensitivity ~50%
- Methotrexate management with (ACOG)
- Absolute contraindications
- Breast-feeding
- Laboratory evidence of immunodeficiency
- Preexisting blood dyscrasias (bone marrow hypoplasia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, or clinically significant anemia)
- Known sensitivity to methotrexate
- Active pulmonary disease
- Peptic ulcer disease
- Hepatic, renal, or hematologic dysfunction/disease
- Coexisting viable IUP
- Does not have timely access to medical institution, or unwilling/unable to comply with post-MTX monitoring
- Relative contraindications
- Adnexal mass >3.5 cm in largest diameter
- Presence of fetal heart rate
- Free fluid visualized in Pouch of Douglas
- Beta-HCG >5000mIU/mL
- Absolute contraindications
- Fun facts
- Hyperemesis gravidarum
- Dfn: loss of 5% of pre-preg weight with n/v/ketosis
- Diagnosis of exclusion!
- 3% of pregnancies
- Dx: exclude other pathologies, check electrolytes, check UA for ketones
- Tx:
- IVF, Pyridoxine B6, Doxylamine
- 2nd line: Metoclopramide
- 3rd line: Odansetron (small risk of fetal cardiac abnormalities)
- UTI and asymptomatic bacteriuria
- Treat every asymptomatic bacteriuria
- Tx:
- Cephelexin
- Amoxicillin
- Nitrofurantoin (ACOG: safe in 2nd and 3rd trimester–avoid in 1st)
- Pyelonephritis: ALWAYS ADMIT
- Acute Appendicitis
- 1st line: US (18% sensitive)
- Gold standard: Noncontrast MRI
- CT if no MRI available, ionizing radiation for single study for appendicitis does not exceed the threshold dose for fetal harm (likely without contrast-gadolinium has fetal mal-effects)
- Tx: surgical intervention, do NOT get sole antibiotic treatment
- REMINDER: Indications for Emergent MRI (at coney)
- Posterior stroke
- Pregnant appendicitis
- Spinal epidural abscess